Yokogawa has developed an ISA100 WirelessTM-based field wireless vibration sensor with the ability to quickly update data as well as a long battery life. By providing real-time updates on vibration levels in plant facilities, the new sensor helps users quickly detect equipment anomalies and enables predictive maintenance.
Since releasing the world’s first ISA100 Wireless-based field wireless devices and wireless systems, Yokogawa has expanded its lineup of field wireless devices that measure temperature, pressure, flow rate, and the like. This new vibration sensor will meet the company’s customers’ needs for a device that can provide the quick updates on vibration levels needed to detect anomalies at an early stage.
Reduction of maintenance workload
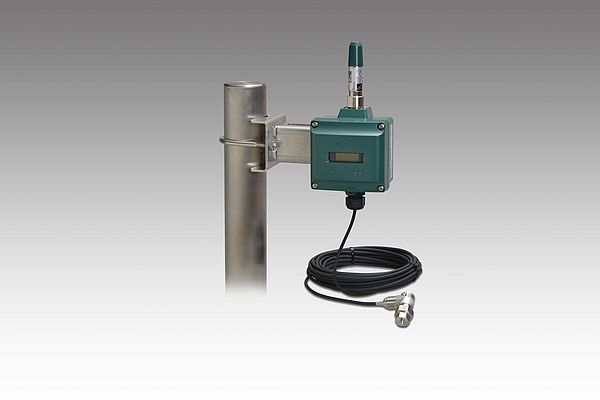
The principal components of this field wireless vibration sensor are the FN510 field wireless multifunction module, the LN01 piezoelectric type acceleration sensor, and the FN110 field wireless communication module. Via a gateway device, the FN510 uses the ISA100 Wireless communications protocol to exchange data with a host-level system such as a DCS. The data collected with this vibration sensor enables plant operators and maintenance staff to monitor vibration levels in real time. Both explosion-proof and non-explosion-proof types are available.
The sensor can be set to update data as quickly as every 10 seconds. This update time is ideal for monitoring vibration levels in plant facilities. When the vibration sensor is set to update data once per minute, it can operate on a single set of batteries for up to 10 years. In addition to eliminating the cost of providing replacement batteries, this reduces maintenance workload. Thanks to the features of ISA100 Wireless and Yokogawa’s technical know-how, the company has achieved a highly reliable wireless network with fully redundant communications that is capable of sending and receiving different types of sensor signals over long distances.