Technology trends & Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 enabling technologies such as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) are helping businesses to develop an increasingly digitalised, connected and data-driven manufacturing landscape. By adopting technologies that support digital transformation strategies, companies can create smart, interconnected factories. The vision of the factory of tomorrow is one of machines, production lines, plants and entire supply chains that communicate with each other to enhance productivity, efficiency and flexibility. The benefits that can be achieved with these frameworks are significant.
A key technology to achieve this is Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN), which was specifically developed by the IEEE 802.1 working group to enhance standard Ethernet and support futureproof capabilities.
TSN functionality
The core benefits offered by TSN are determinism and convergence.
Determinism is fundamental to supporting time-critical communications on the factory floor, as it ensures the predictable delivery of data by minimising latency and jitter. This, in turn, supports real-time applications and provides the foundation for convergence.
Convergence, the second key ability of TSN, enables companies to merge different traffic types onto a single network without affecting the performance of shop floor communications. This is fundamental to sharing operational insights and hence increasing process transparency across an enterprise, which can then be used to derive insights to optimise manufacturing facilities and entire organisations.
Since TSN is an extension of standard Ethernet, it is also interoperable with existing network technologies and devices. Hence it can be used alongside existing devices, reducing system investments.
TSN market opportunities
TSN is recognised across different sectors as the future of industrial Ethernet and industrial communications. Consequently, interest in and adoption of this technology are growing.
These trends offer particularly exciting commercial opportunities for automation device vendors. By developing and releasing state-of-the-art products with TSN capabilities, vendors can increase their market coverage and gain a competitive advantage.
To help vendors understand how to leverage this opportunity, the following chapters of this white paper will discuss the technology behind TSN, its development workflow and the methods available to develop compatible automation products.
Overview of TSN technology
TSN technology is defined by IEEE 802.1 standards, the most important for industrial communications being IEEE 802.1AS and IEEE 802.1Qbv, as they are at the core of deterministic performance and convergence.
More precisely, the IEEE 802.1AS standard provides mechanisms to synchronise all devices within a network with high accuracy, thus supporting precise control of latency and jitter for transmissions across the network. This in turn defines predicable behaviour and provides the basis of determinism.
Using the network-wide time reference provided by IEEE 802.1AS, IEEE 802.1Qbv temporally organises the data transmissions based on their respective priorities, facilitating the convergence of different types of data traffic in a deterministic manner.
To achieve this, the time-aware shapers (TASs) defined by IEEE 802.1Qbv make network switches aware of the cycle times for real-time traffic. The periodic time windows created by the TASs, reproducing a Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) model, make possible to merge different types of traffic and prioritise any urgent data. As the timing parameters of the TASs are shared by fully synchronised network devices, these are aware of when time-critical data are sent and received.
In effect, some of these time intervals can be scheduled and reserved for priority time-critical traffic, while non-time-critical, best-effort traffic is held to avoid any interference. Departure and arrival times of this traffic are therefore predetermined. In this way, TSN can ensure deterministic communication for hard real-time applications.
Also, the ability to support network convergence enables users to blur the lines between operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT).
Overview of TSN development workflow
It is clear why offering TSN-compatible products is highly beneficial for automation vendors. To successfully develop devices that provide added value to end users, it is necessary to consider the capabilities, performance and nature of the products themselves from the outset.
First, companies need to clearly define what the product should be able to do. This will determine the type of station that is to be developed, such as master or remote. Also, the required performance level, in terms of speed and synchronisation accuracy, needs to be decided. Once these features are set, vendors can look for existing products that may be suitable for an upgrade to deliver TSN functions.
Businesses then need to select the most suitable development method for the TSN device that they are producing. The decision should be based on the pre-identified performance requirements, along with a consideration of the suitability of their existing development methods.
Another key decision that companies need to make is where to conduct the product development activities. Should these be carried out using in-house resources? Or is it best to rely on a specialist contractor?
Once the TSN device is ready, it also needs to be certified in order to prove that the necessary technology requirements are met. To do this, vendors should undertake relevant third-party certification. This offers an independent assessment of the communications performance that can offer extra assurance to customers.
When all these tasks have been completed, the TSN-compatible device can be introduced to the market.
TSN development methods
In order to implement TSN for industrial communications, end users and OEMs need both a suitable network technology as well as automation devices that can support this technology’s capabilities. This need is met by vendors offering innovative products, which address customers’ needs while increasing their competitive advantage in the marketplace. In general, to minimise costs and time to market, a vendor will look to use their existing platforms and tools where possible to develop these products. Hence it is important that the type of industrial Ethernet technology used offers an open development ecosystem that includes options that match the vendors’ existing methods. The broader the range of options, the better chance there is of catering to the needs of the most vendors. Typically, this means there should be both hardware and software solutions in addition to different bandwidth options, such as 100Mbit and gigabit.
New design or migrate existing products?
Once the type of station has been selected, vendors should decide if they should add TSN capabilities to an existing product, or if new product development will be necessary. In the case of a new product, after taking market requirements into account, a specification that fixes what the new TSN-compatible products should do, the capabilities they should offer and the investment required to implement this is essential. These elements are key to defining the performance, ease of implementation and time-to-market.
Software solutions
A software protocol stack, or just “stack” is a collection of independent components that work together to support the execution of an application. Device makers should check the specification of the software stack they intend to utilise to ensure compliance. A TSN stack is typically part of a software development kit (SDK). Software methods offer perhaps the fastest solution to provide TSN capabilities to existing products, as they reduce in-house development time and costs for vendors. Furthermore, they are generally portable, so they can be applied with minimal changes. Hence, they offer a versatile solution to businesses interested in quickly implementing TSN.
Hardware solutions
In order to harness the full potential of TSN, it may be beneficial to consider a hardware-based solution. While this route may require more investment and development time, the benefit is a more competitive product and longer lifecycle. Several different solutions are available, enabling vendors to select the right platform for their needs. Among them can be found Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), also referred to as dedicated communication Large Scale Integration (LSI), built-in/embedded modules, or FPGA/IP core. In regard with specialised applications, developers can also rely on TSN-compatible PC boards to implement key capabilities on industrial/ standard PCs and similar devices within advanced industrial Ethernet networks. This allows the connection of PCs without any special development. This is especially useful in edge computing applications where a PC/IPC may be used as the gateway to higher level IT systems, providing a component of an OT/IT converged system.
The importance of conformance testing
To validate the capabilities of TSN-compatible devices, developers need to conduct thorough conformance testing, i.e. confirm that the product complies with all the requirements of a given network standard and that it is correctly implemented.
Conformance and interoperability testing can be performed in-house by vendors and/or by independent organisations. Since end users usually look for an independent third-party certification, in house testing is generally only used to confirm that a product is ready to be tested by a third party. In effect, third-party testing provides an impartial and unbiased evaluation from an external source.
Finally, as conformance testing is conducted by a third-party, automation vendors can focus on development activities whilst specialised engineers assess the products.
Industrial Ethernet protocols that support TSN
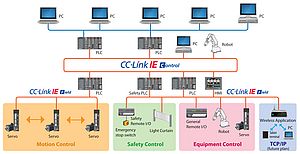
To quickly deliver innovative TSN-compatible products for industrial automation applications and tap into this market, businesses need to leverage proven network technologies, such as CC-Link IE TSN. This is an open network that combines TSN functions, as defined by IEEE 802.1 AS and Qbv standards, with gigabit bandwidth.
By selecting this solution, product developers can benefit from a comprehensive development ecosystem that supports the creation of master, local and remote stations.
Moreover, the CLPA can support vendors by assessing the conformance of their products, ensuring compatibility with CC-Link IE TSN specifications.
Another advantage is that the product can be included in the CLPA’s online catalogue, making it visible to customers worldwide. Joint promotion with the CLPA is also possible
Conclusions
TSN is a key enabling technology for the digital transformation of manufacturing, and can offer four key benefits for end users and OEMs:
• Simpler network architectures/machine designs
• Greater process transparency and better management
• More productivity
• Better integration of OT and IT systems
To enable futureproof industrial communications and next-level performance, automation vendors need to act now to deliver TSN-compatible products or upgrade existing devices with TSN capabilities. By doing so they can help their customers to create the factories of the future whilst enhancing their own competitiveness in a fast-growing market.
John Browett, General Manager at CC-Link Partner Association (CLPA)
john.browett@eu.cc-link.org
www.linkedin.com/in/johnbrowett/
Link to the overall supplement (IEN Europe March)
CLPA Contact
Virtual Exhibition Stand: http://cc-link-ve.eu/
CLPA Europe Homepage: https://eu.cc-link.org/en/
CLPA North Americas Homepage: http://am.cc-link.org/en/
Connect with the CLPA on social media:
www.linkedin.com/company/cc-link-partner-association-europe
www.linkedin.com/company/clpa-americas
https://twitter.com/CC_LinkNews
https://twitter.com/CC_LinkNewsDE
https://twitter.com/CC_LinkNewsIT
https://www.xing.com/companies/cc-linkpartnerassociationeurope
www.youtube.com/c/CCLinkPartnerAssociation